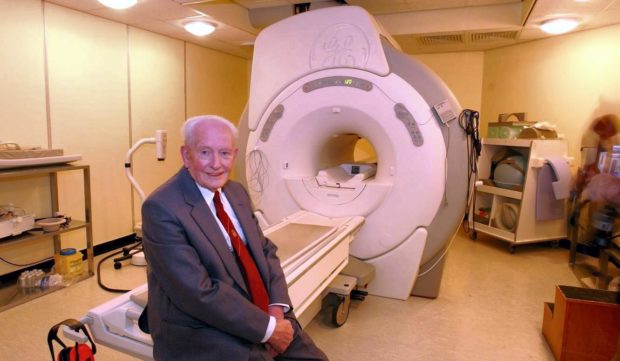
John Mallard, the pioneering Aberdeen physicist who helped create the world’s first full-body MRI scanner, has died at the age of 94.
Under his leadership, a team from Aberdeen University built the scanner, which clinicians used to carry out the world’s first body scan of a patient from Fraserburgh.
The machine was used to scan mice originally before moving onto to scan humans.
It is now used across the world and has saved many lives.
A prototype of the scanner is now on display at the National Museum of Scotland.
Speaking to the Evening Express in 2016, he spoke of his “pride” in helping to produce the machine.
He said: “I am delighted that the MRI scanner has helped to save so many lives over the years.
“It was a team of many scientists who helped to create the first one, it didn’t all come from me.”
Professor Mallard was appointed the university’s first Professor of Medical Physics in 1965 and was influential in championing PET scanning technology and led the drive to bring a facility to the granite city.
He drove forward a national fundraising campaign to pay for a building next to Woodend Hospital to house a second-hand scanner.
The old facility has since been replaced by the state-of-the-art John Mallard PET Centre at Aberdeen Royal Infirmary.
He has been widely celebrated across the city and was awarded an OBE in 1992, the same year he retired from the university.
Prof Mallard was also awarded the Freedom of the City of Aberdeen in 2004 for his pioneering work in medical imaging.
Those who worked with him paid tribute to the “pioneer” whose legacy lives on through the MRI technology that is used daily around the world.
Professor Siladitya Bhattacharya, Head of the University of Aberdeen’s School of Medicine, Medical Sciences and Nutrition, said: “We are deeply saddened to learn of the passing of Professor John Mallard who, along with his team helped change the face of medical imaging.
“His legacy lives on through the technology that saves lives on a daily basis and we are proud that he carried out such ground-breaking work at the University of Aberdeen.
“Our thoughts are with his family at this time.”
Emeritus Professor Peter Sharp OBE, who worked for Professor Mallard and then became his successor, added: “Professor John Mallard played a major role in the development of Medical Physics, both here in the UK and abroad.
“Appointed as the first holder of the Chair in Medical Physics in Aberdeen – also the first such chair in Scotland – his tenacity and “can do” approach led to a remarkable series of developments in medical imaging, culminating in his group building the first whole-body clinical MRI machine.
“It is no understatement to say that hundreds of thousands of patients worldwide have benefited from his vision for medical imaging.”
Professor David Lurie, who worked under Professor Mallard and is now leading the next generation of MRI technology at the University of Aberdeen, said: “Professor John Mallard was a pioneer, leading light and world-recognised authority in Medical Physics who led the development of novel scanning technology that is still benefitting doctors and patients today.
“In the mid-1970s I worked in John Mallard’s department as a “summer student”.
“Then, in 1983, he appointed me as a postdoctoral researcher within the MRI team. Soon afterwards, he suggested that I work on free radical imaging, and that research eventually led to my own team’s work on Fast Field-Cycling imaging, which is still in progress today.
“There is no doubt that I owe my career to John Mallard, and I am extremely grateful to him for that.
“During the years that I worked for him, I found John Mallard to be a strict, very fair manager.
“When a memo from him appeared – this was long before email, I knew that there would be no question of an extension of any deadline, but equally his suggestions, or “commands”, were always pertinent and frequently paid scientific dividends.”
Read more on Professor John Mallard
https://www.pressandjournal.co.uk/fp/nostalgia/2372396/highlighting-aberdeens-trailblazing-medical-pioneers-whose-work-helped-millio