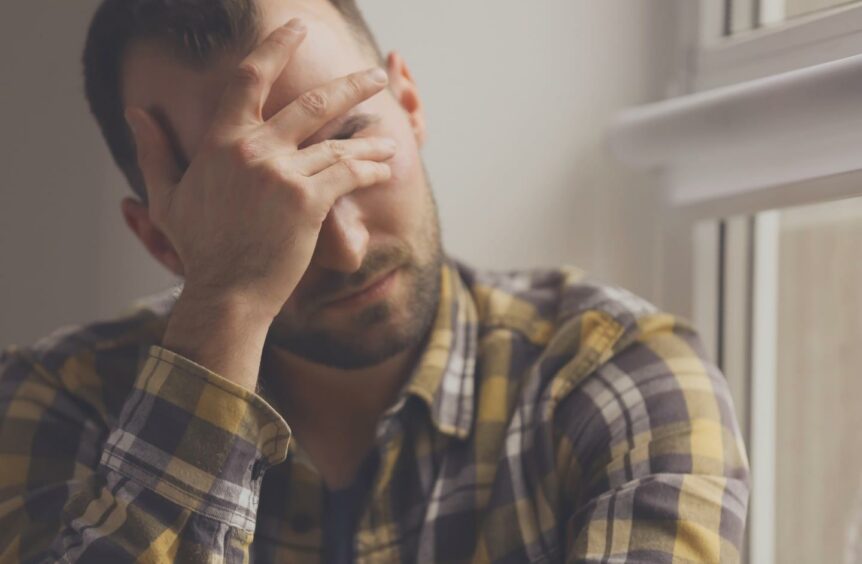
As the nights get longer and the weather gets colder, three in every 100 people in the UK will face Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
SAD is a form of depression that usually in and autumn and can drag on through the winter months.
Sometimes referred to as “winter gloom”, the seasonal condition can make people feel like their energy levels are deflating.
However, the Men’s Health Forum found men are 20% less likely to see their GP than women for health conditions, which could mean SAD can go unnoticed and undiagnosed in many.
Earim Chaudry, medical director of men’s health platform Manual, has listed some of the main causes for men suffering from the condition, and some treatments available.
What causes seasonal affective disorder?
The exact cause of SAD is not known, but the NHS has cited reduced sunlight hours as the main contributing factor.
Increased levels of melatonin and lower serotonin levels are also plausible causes.
Melatonin is a hormone found in a pea-shaped gland in the brain called the penial gland.
It is primarily released at night, and has long been associated with control of the sleep-wake cycle.
People with SAD are more likely to release more melatonin, which can make them sleepier.
Body’s natural clock is thrown off
As winter days become darker, melatonin production increases, and those with SAD can feel overtired and lethargic, which can contribute to depression.
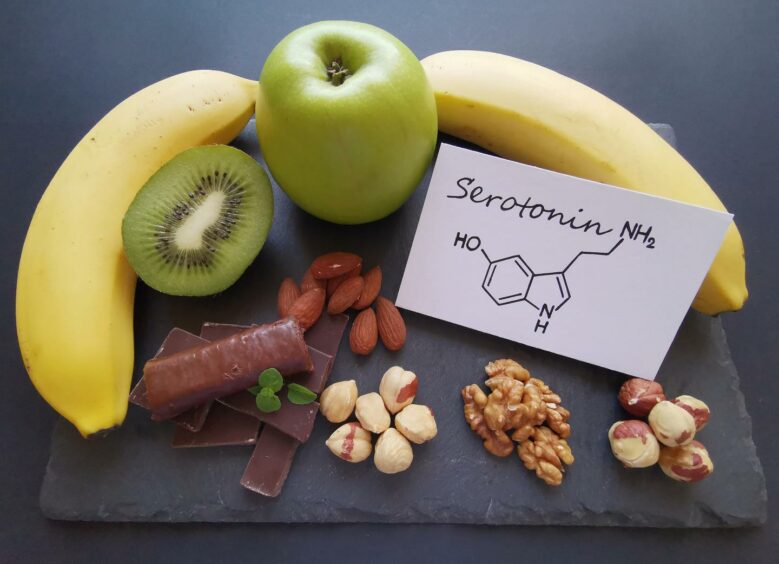
Serotonin is a hormone that affects your mood, appetite and sleep. A lack of sunlight may lead to lower serotonin levels, which can be linked to feelings of depression.
Research shows that high levels of serotonin in the brain are linked to elevated mood and feeling happy, whereas low levels are linked to the symptoms of depression, including feeling sad, upset, and generally low in mood.
Another probable cause of SAD is the disruption of your body’s natural internal clock, called the circadian rhythm.
The human body uses sunlight to time various important functions, including when you wake up, so lower light levels during the winter may disrupt your body clock.
How can you treat ‘winter gloom’?
Dr Chaudry has provided some tips on how to combat the winter gloom, starting with what you eat.
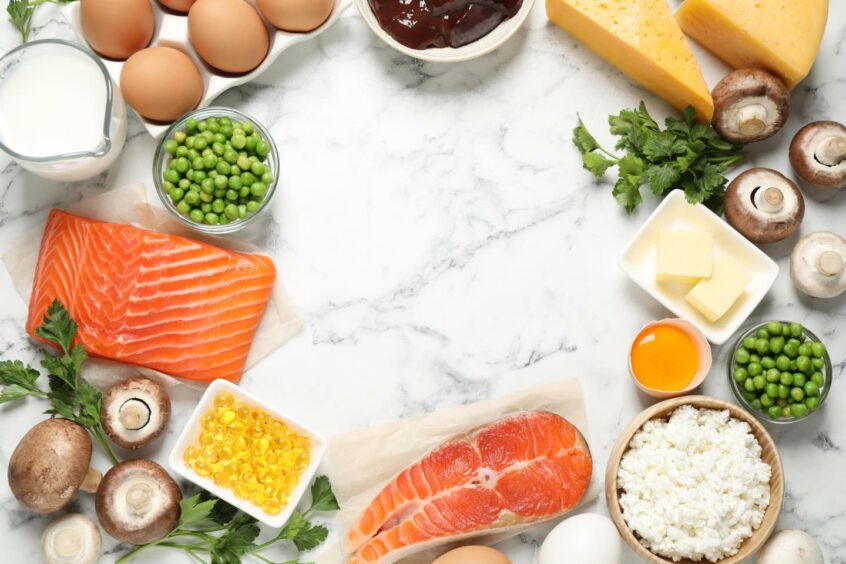
Vitamin D, also known as the “sunshine vitamin”, is essential for the winter months and should be incorporated into your diet.
Foods to include are oily fish, eggs and mushrooms. Supplements can also be taken to make sure you’re getting enough vitamins.
Dark, leafy greens high in Vitamin A, calcium and Vitamin C should also be eaten.
Some people find that light therapy can help improve their mood.
The light produced from a special SAD lamp can encourage your brain to reduce the production of melatonin and increase the production of, which can in theory help fight depression.
Sunrise alarm clocks, which gradually brighten up your bedroom as you wake up, are also an option.
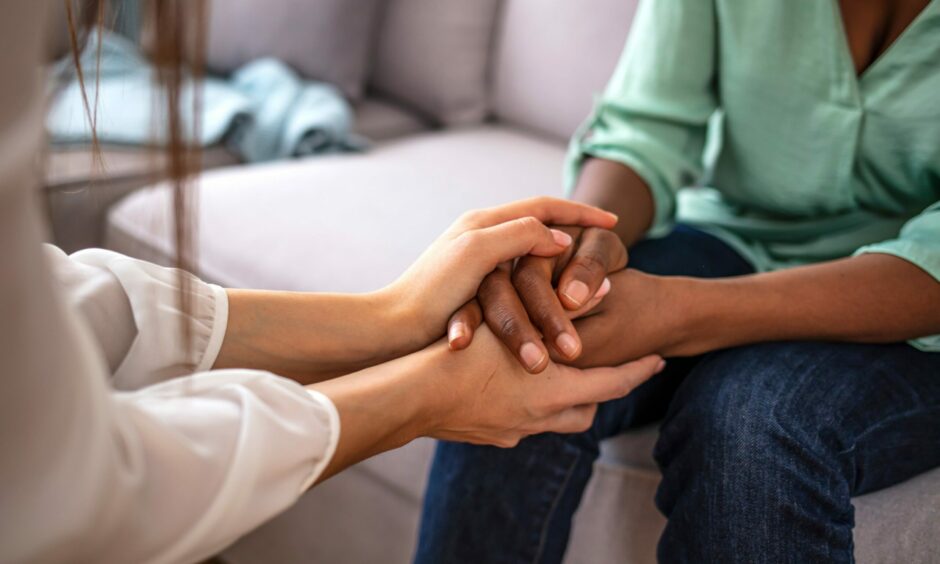
Talking therapy can help change negative thoughts
Psychotherapy, sometimes called talking therapy, is also effective.
It can be used to help a person change behaviour, increase happiness and overcome problems.
The main purpose is to change negative thoughts and behaviours that may be making you feel worse.
During psychotherapy, you can learn about your condition, and work with a professional on how to treat this.
Speak with your GP for more information about psychotherapy.